Tuning Your Processor: Maximizing CPU Performance Through Overclocking
In the world of computing, maximizing the performance of your central processing unit (CPU) is essential for achieving peak efficiency and speed. Whether you're a gamer, content creator, or simply a power user, understanding how to tune your processor can make a significant difference in your overall computing experience. In this guide, we'll explore the art of CPU tuning, providing you with valuable insights and techniques to unlock the full potential of your processor.
-
Improved Performance: Adjusting the CPU settings can lead to higher clock speeds and faster processing, resulting in smoother multitasking and better overall performance.

-
Enhanced Efficiency: Fine-tuning the CPU can also improve power efficiency, allowing your system to deliver better performance while consuming less power.
-
Extended Lifespan: Contrary to popular belief, proper CPU tuning can actually extend the lifespan of your processor by ensuring it operates within safe temperature and voltage limits.
-
CPU Cooling: Efficient cooling is crucial for maintaining optimal CPU performance. Investing in a high-quality cooling solution, such as liquid cooling or a robust air cooler, can help keep your processor temperatures in check during overclocking.
-
Stability Testing: After making adjustments to your CPU settings, it's vital to conduct stability tests to ensure that your system can handle the changes without crashing or encountering errors. Tools like Prime95 and MemTest86 can help you stress-test your CPU and memory for stability.
-
Voltage Control: Adjusting the voltage settings of your CPU can significantly impact its performance and power consumption. However, it's essential to proceed with caution, as excessive voltage adjustments can lead to instability and hardware damage.
-
Understand Your Hardware: Before you begin overclocking, take some time to familiarize yourself with your CPU and motherboard. Determine the model of your CPU, its base clock speed, and its maximum safe operating temperature. Additionally, check your motherboard's BIOS or UEFI interface to ensure it supports overclocking and has the necessary options available.
-
Enter BIOS/UEFI Interface: Restart your computer and enter the BIOS or UEFI interface by pressing the designated key during the boot process (usually Del, F2, or F10). Once inside the BIOS/UEFI, navigate to the CPU settings menu, where you'll find options for adjusting the core clock speed, multiplier, and voltage.
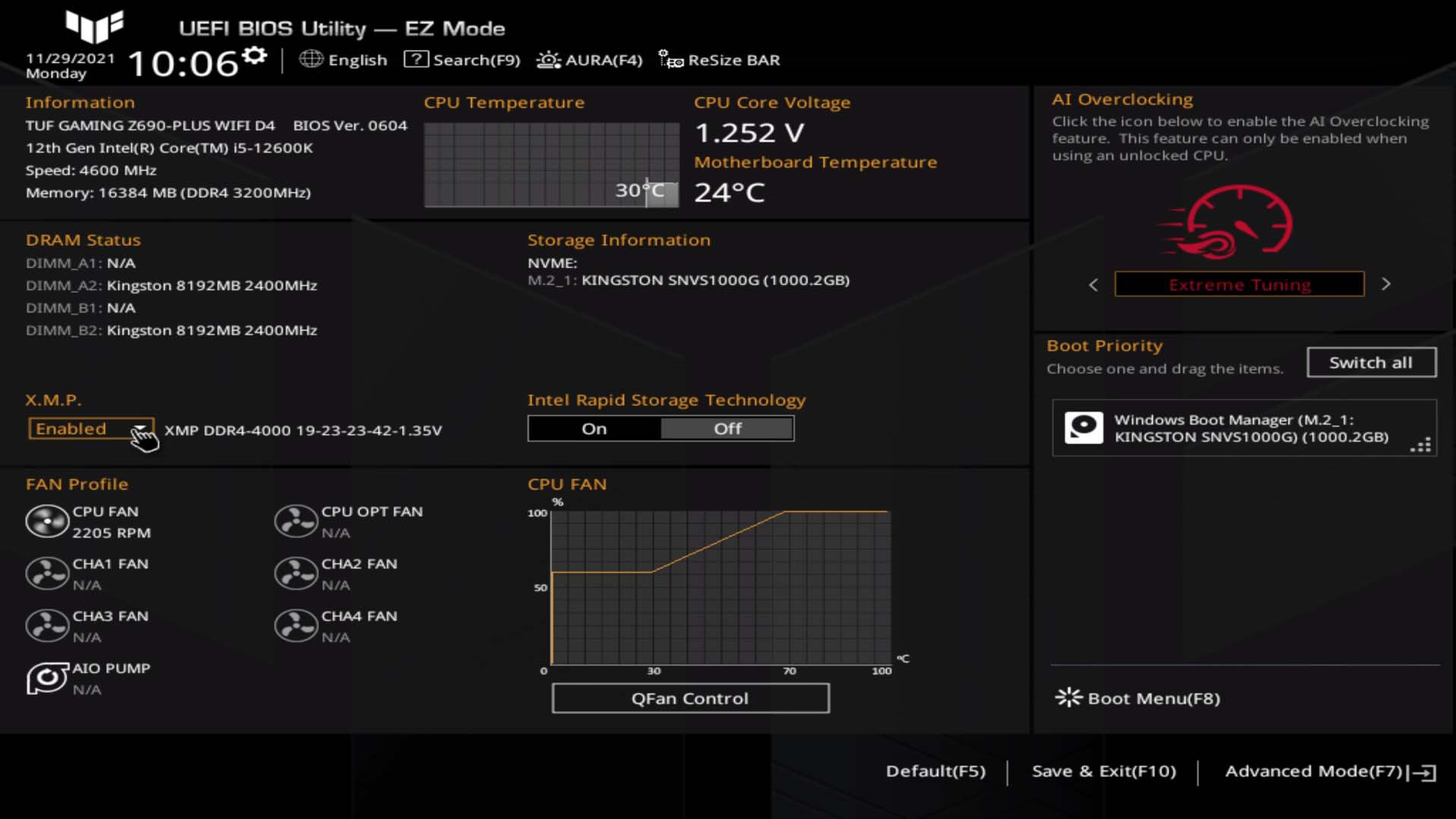
-
Start Slow: Begin your overclocking journey by making small, incremental adjustments to the core clock speed (also known as the base clock) or multiplier. Increase the clock speed by 100 MHz at a time, then save your changes and exit the BIOS/UEFI interface. Reboot your system and run stress-testing software like Prime95 or AIDA64 to test for stability.
-
Monitor Temperatures: During stress tests, keep a close eye on your CPU temperatures using monitoring software like HWMonitor or Core Temp. Ensure that temperatures remain within safe limits (usually below 80°C) to prevent overheating and potential damage to your CPU.
-
Test for Stability: After applying overclocking settings, it's crucial to test for stability to ensure your system can handle the increased performance without crashing or encountering errors. Run stress tests for extended periods (at least 30 minutes to an hour) to simulate real-world usage scenarios.
-
Adjust Voltage Settings: If you encounter instability during stress tests, you may need to adjust the CPU voltage (Vcore) to provide additional power to the overclocked CPU. Increase the voltage gradually in small increments, then retest for stability. Be cautious not to exceed recommended voltage limits to avoid damaging your CPU.
-
Fine-Tune and Iterate: Continue fine-tuning your overclocking settings by adjusting clock speeds, multipliers, and voltages until you find the optimal balance between performance and stability. Keep in mind that overclocking is an iterative process, and it may take several attempts to achieve the desired results.
-
Record Your Settings: Once you've achieved a stable overclock, record your settings in a safe place for future reference. This includes the core clock speed, multiplier, voltage, and any other relevant parameters. Having a record of your settings will make it easier to revert to a stable configuration if needed.



